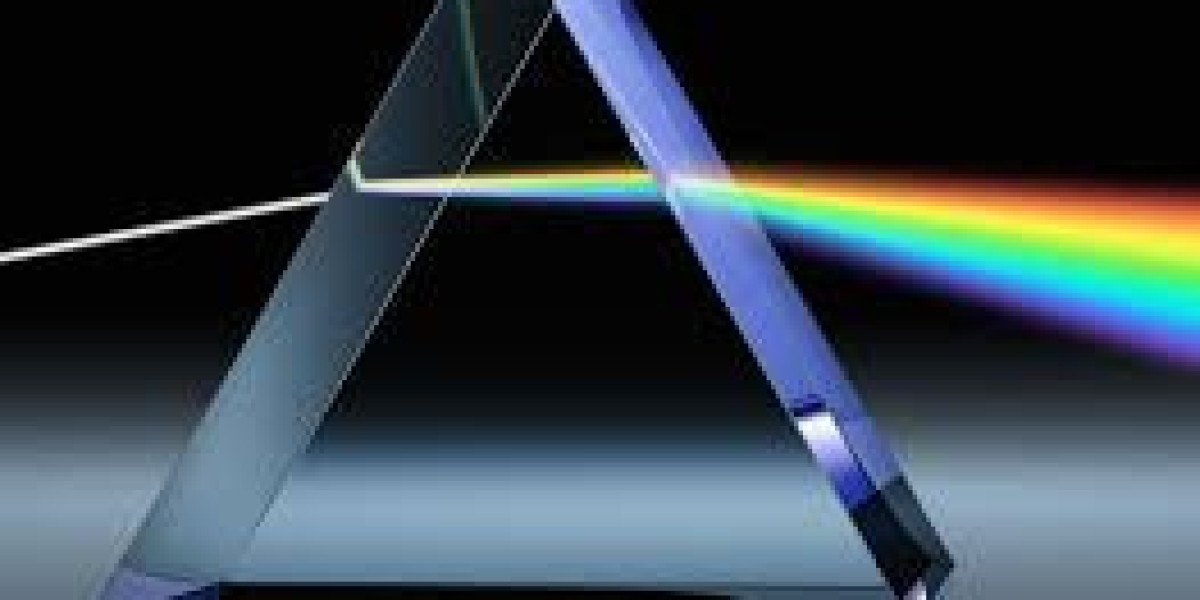
Many engineers, optical designers, researchers, and technicians face the same frustrating issue: their imaging systems, measurement tools, or light-based instruments do not produce accurate, stable, or high-contrast results. Even after upgrading lenses or sensors, the output still feels inconsistent. The real problem often lies in the one component people overlook—light direction and refraction control.
A high-precision prism is one of the most effective solutions for improving beam alignment, splitting, redirection, and optical stability across a wide range of applications.
Why Optical Systems Fail Without a Quality Prism
1. Unstable Beam Alignment
Without proper refraction control, even a small deviation in angle causes major accuracy issues in imaging, inspection, and measurement systems. Regular glass blocks light but cannot redirect it precisely.
2. Light Loss and Poor Transmission
Low-quality components scatter or absorb light, reducing clarity and brightness. This impacts everything—from microscope imaging to laser systems and AR modules.
3. Distorted Image Quality
If the internal optical path is misaligned, the final image becomes stretched, blurred, or color-shifted. Many users blame sensors, but the root issue is often poor beam pathway design.
4. Limited Durability in Harsh Environments
Heat, vibration, and humidity affect unstable materials. A standard glass piece cannot maintain consistent refractive performance under industrial, medical, or scientific conditions.
How a Precision Prism Solves These Problems
1. Exact Light Redirection
A prism is engineered to bend, split, and guide light with exceptional accuracy. This ensures that beams travel exactly where they should, stabilizing the entire optical system.
2. High Optical Clarity
Premium prisms offer excellent transmission with minimal scattering. This improves image brightness, contrast, and color accuracy—essential for cameras, AR optics, and inspection tools.
3. Stable Refractive Index
Quality prisms maintain consistent performance under temperature changes, vibrations, and environmental stress. This stability ensures long-term reliability for precision devices.
4. Versatile Functionality
Prisms can:
Reflect light internally
Split beams into multiple paths
Combine two images
Adjust viewing angles
Correct distortion
Enhance stereoscopic or 3D imaging
They are one of the most flexible optical components available.
For the best results, many professionals rely on high-grade optical prism designs tailored for clarity, alignment, and durability.
Where Prisms Are Most Critical Today
Optical Instruments & Microscopy
Prisms enhance light pathways to improve contrast, stability, and field of view in microscopes and lab equipment.
Laser Systems
They ensure beam accuracy for cutting, measurement, scanning, and alignment applications.
Cameras & Imaging Devices
Prisms help redirect and split light, improving image quality in compact camera modules and high-end photography systems.
AR/VR Optics
Precise redirection supports immersive visuals and stable visual pathways in advanced wearable displays.
Medical & Scientific Tools
Endoscopes, spectrometers, and diagnostic devices depend on accurate optical pathways, which prisms help maintain.
Conclusion
If your optical system struggles with alignment issues, weak imaging results, or unstable light transmission, the missing piece may be a high-quality prism—not a new sensor or lens. A precision prism improves clarity, maintains beam accuracy, and delivers long-term optical stability. Whether you're designing new optical hardware or upgrading existing equipment, adding the right prism is one of the most reliable ways to enhance performance instantly.